Trump’s war on climate science is pushing us into a dystopian future
Trump’s war on climate science is pushing us into a dystopian future
US President Donald Trump’s latest war on the climate includes withdrawing support for any research that mentions the word.
He has also launched a purge on government websites hosting climate data, in an apparent attempt to make the evidence disappear.
Yes, it’s bad, especially for US-based scientists. It also affects scientists in Australia and the rest of the world. But there are ways to get around the problem. There might even be a silver lining to this dark cloud.
Trump cannot stop global climate action, although he might slow it. Nor can he hide the truth by restricting access to data. Climate research will continue despite Trump’s best efforts to hamstring scientists and research institutions.
No strength in ignorance
Last year was the warmest on record, a fact that yet again confirms our worst-case predictions. The world has already surpassed the (arbitrary) 1.5°C threshold increase relative to pre-industrial temperatures — a threshold that only a few years ago we didn’t think we would cross until 2030 at the earliest.
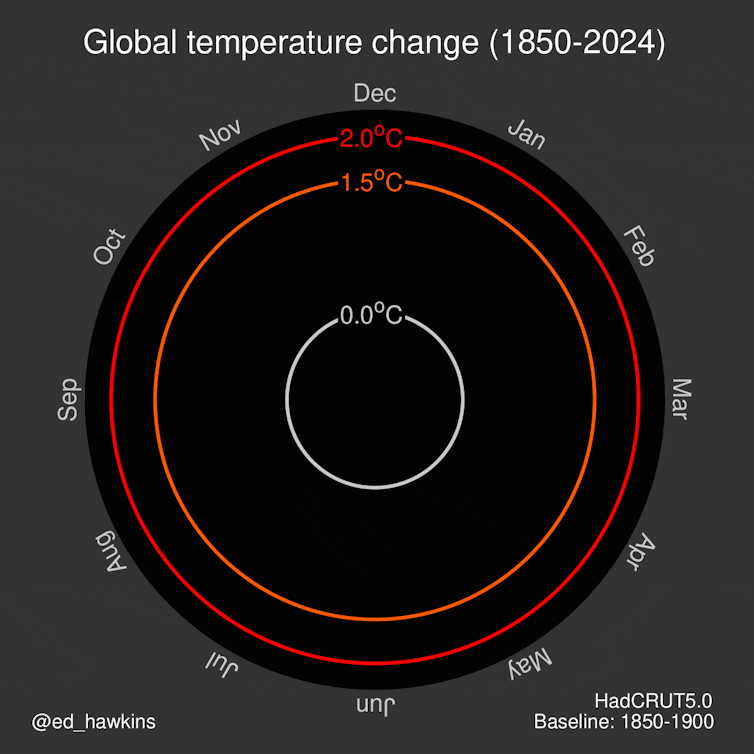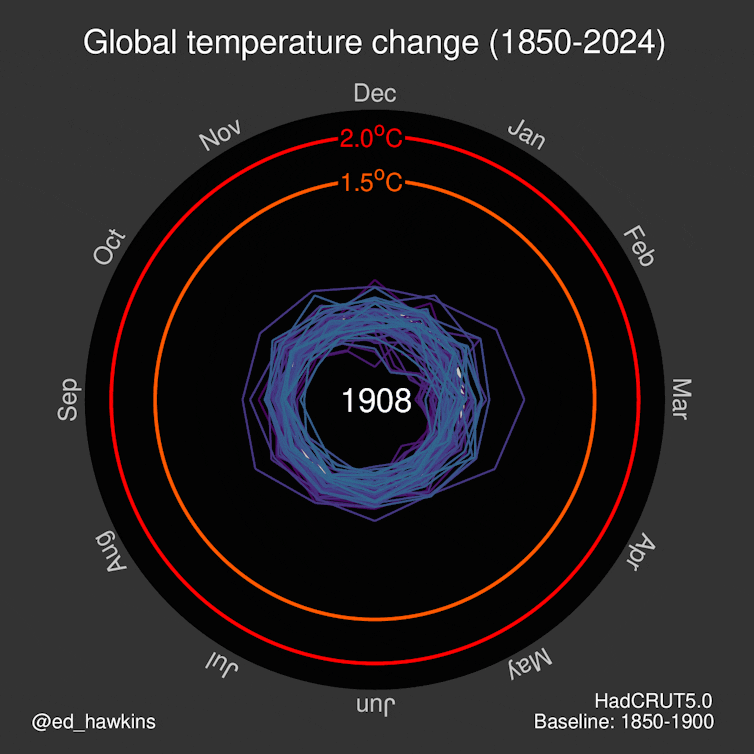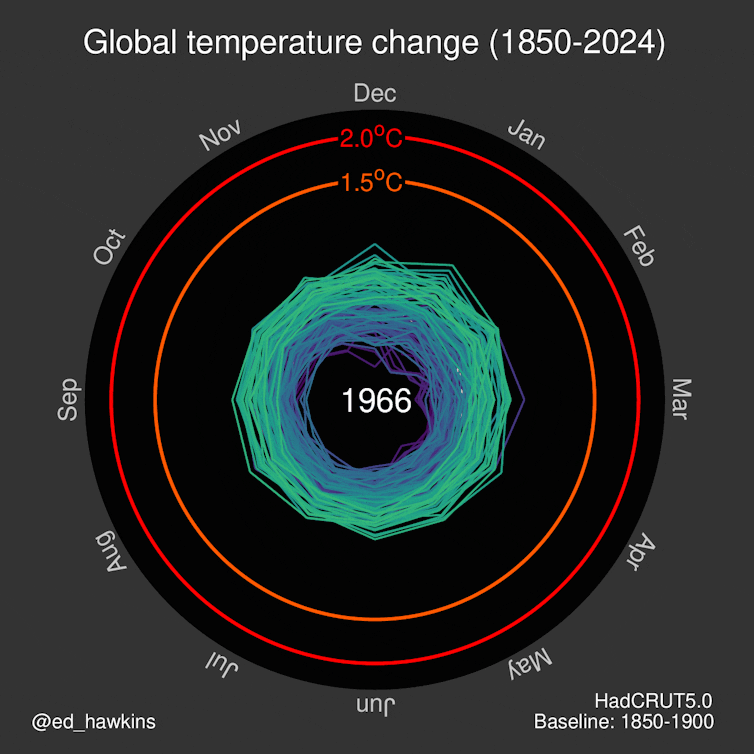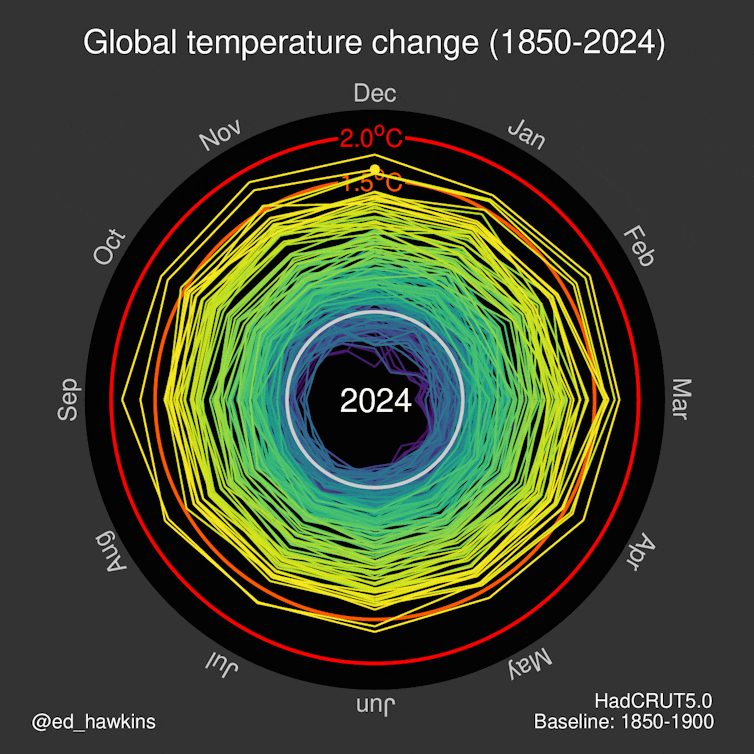
We’re now on track to be living in a world that’s 3°C hotter or more by the end of the century.
Understand how AI is changing society
This is despite more than 30 years of global commitments that have largely failed to bend the warming trend.
But ignoring climate change won’t make it go away. Like the Ministry of Truth in George Orwell’s classic dystopian novel, 1984, Trump seems to believe “ignorance is strength”. He’s trying to erase facts about the climate crisis, perhaps to keep people ignorant and subdued.
What this means for Australian climate science
Many Australian scientists (including me) collaborate regularly with US colleagues, share funding, and publish results together. Knowledge sharing and open-access data are the foundation of advances in science, so Trump’s assault will inevitably slow progress here.
For example, Australian and US scientists regularly collaborate in big-ticket research and policy development related to climate change, such as the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change’s Physical Science Basis reports. But even with fewer US scientists in the mix, the research and reporting will continue.
Students involved in climate research will also be negatively affected, with fewer opportunities for scholarships and exchanges between our two countries.
It’s worth remembering the US is not the only country with global data sets that measure the magnitude of the climate calamity. Australia’s own Bureau of Meteorology, CSIRO, Terrestrial Ecosystem Research Network, Integrated Marine Observing System, and Geoscience Australia are just some of examples of Commonwealth government-backed data custodians that are immune to the US purge.
Other reputable climate-data repositories around the world include the European Union’s Climate Data Store, the University of East Anglia’s Climate Research Unit, the Netherlands Meteorological Institute’s Climate Explorer, and the independent WorldClim, to name a few.
While restricting access to US-based websites is inconvenient, we can readily get around the problem. Many of my colleagues have also been downloading data prior to the purge mandate to maintain access.

Consequences for the US
Over the past month I have been inundated with horror stories from many US-based colleagues in academia and the public service, who have lost their jobs and/or research funding. In addition to these very real personal tragedies, the bigger picture is even bleaker.
The loss of scientific and technical expertise these mass sackings entail weakens the capability of the US workforce to discover and develop solutions to climate change. Just when we need good scientific and engineering innovations more than ever, a massive capacity is being erased before our eyes.
Trump’s fear and hatred of all things “climate” also foreshadows even more greenhouse gas emissions from the US. He has issued various strong-arm orders to “unleash American energy” by fast-tracking fossil-fuel exploitation, blocking offshore wind-power development, and revoking targets for electric vehicles, for example.
More emissions mean more climate change, especially when you’re already one of the biggest contributors to the global problem. The US is the second-highest greenhouse emitter in the world, behind only China.
Trump claims his actions will improve economic prosperity. The reality is they will instead retard the green manufacturing boom. Curtailing anything with even the faintest whiff of “climate” will in fact reduce economic prosperity and increase unemployment.
Costs to the rest of the world
On his first day as president, Trump withdrew the US from the Paris climate agreement. This effectively removes his country from all binding limits on actions that contribute to climate change.
Weakening international treaties is a two-edged sword, because it not only lets the US off the leash, it also potentially discourages other nations from acting responsibly. Analogous to the “unresponsive bystander effect”, many nations may now be more hesitant to commit to reductions because one of the biggest emitters refuses to do anything about it.
Trump has also slashed US international aid, which will slow climate action in countries that need the most assistance.
Overall, faster rates of warming will inevitably put more strain on natural resources and agricultural production. This could increase the probability of international warfare over water, food and other essential natural resources. Because autocratic countries cope worse with food shortages than democratic ones, climate emergencies will penalise nations led by despots more heavily.

Finding a silver lining
Trump’s foolhardy anti-climate campaign is enough to make many people despair. But there are a few faint glimmers of hope on the horizon.
As the US shirks its domestic and international responsibilities, other countries might resolve to do more. Not relying on the US could force capacity-building elsewhere. Some even suggest without the US at the table slowing progress, stronger climate action might result.
Americans have their own daunting fight on their hands. But the rest of the world will have to take up the slack if we have any chance of limiting the health, wealth, equality, human rights and biodiversity calamities now unfolding because of climate change.
대화 참여하기